16.从零开始:SpringBoot配置动态刷新的详细解析与实践!
关于SpringBoot的自定义配置源、配置刷新之前也介绍过几篇博文;最近正好在使用apollo时,排查配置未动态刷新的问题时,看了下它的具体实现发现挺有意思的;
接下来我们致敬经典,看一下如果让我们来实现配置的动态刷新,应该怎么搞?
I. 配置使用姿势
既然要支持配置的动态刷新,那么我们就得先看一下,在SpringBoot中,常见的配置使用姿势有哪些
1. @Value注解绑定
直接通过@Value注解,将一个对象得成员变量与Environment中的配置进行绑定,如
@Slf4j
@RestController
public class IndexController
@Value("${config.type:-1}")
private Integer type;
@Value("${config.wechat:默认}")
private String wechat;
private String email;
@Value("${config.email:default@email}")
public IndexController setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
return this;
}
}
注意:@Value支持SpEL
2. @ConfigurationProperties绑定
通过@ConfigurationProperties注解声明一个配置类,这个类中的成员变量都是从Environment中进行初始化
如:
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "config")
public class MyConfig {
private String user;
private String pwd;
private Integer type;
}
3. Environment.getProperty()直接获取配置
直接从上下文中获取配置,也常见于各种使用场景中,如
environment.getProperty("config.user");
II. 配置刷新
接下来我们看一下,如何实现配置刷新后,上面的三种使用姿势都能获取到刷新后的值
1. 自定义一个属性配置源
自定义一个配置源,我们直接基于内存的ConcurrentHashMap来进行模拟,内部提供了一个配置更新的方法,当配置刷新之后,还会对外广播一个配置变更事件
public class SelfConfigContext {
private static volatile SelfConfigContext instance = new SelfConfigContext();
public static SelfConfigContext getInstance() {
return instance;
}
private Map<String, Object> cache = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
public Map<String, Object> getCache() {
return cache;
}
private SelfConfigContext() {
// 将内存的配置信息设置为最高优先级
cache.put("config.type", 33);
cache.put("config.wechat", "一灰灰blog");
cache.put("config.github", "liuyueyi");
}
/**
* 更新配置
*
* @param key
* @param val
*/
public void updateConfig(String key, Object val) {
cache.put(key, val);
ConfigChangeListener.publishConfigChangeEvent(key);
}
}
/**
* 主要实现配置变更事件发布于监听
*/
@Component
public class ConfigChangeListener implements ApplicationListener<ConfigChangeListener.ConfigChangeEvent> {
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ConfigChangeEvent configChangeEvent) {
SpringValueRegistry.updateValue(configChangeEvent.getKey());
}
public static void publishConfigChangeEvent(String key) {
SpringUtil.getApplicationContext().publishEvent(new ConfigChangeEvent(Thread.currentThread().getStackTrace()[0], key));
}
@Getter
public static class ConfigChangeEvent extends ApplicationEvent {
private String key;
public ConfigChangeEvent(Object source, String key) {
super(source);
this.key = key;
}
}
}
接下来就需要将这个自定义的配置元,注册到 environment 上下文,在这里我们可以借助ApplicationContextInitializer来实现,在上下文初始化前,完成自定义配置注册
public class SelfConfigContextInitializer implements ApplicationContextInitializer<ConfigurableApplicationContext> {
@Override
public void initialize(ConfigurableApplicationContext configurableApplicationContext) {
System.out.println("postProcessEnvironment#initialize");
ConfigurableEnvironment env = configurableApplicationContext.getEnvironment();
initialize(env);
}
protected void initialize(ConfigurableEnvironment environment) {
if (environment.getPropertySources().contains("selfSource")) {
// 已经初始化过了,直接忽略
return;
}
MapPropertySource propertySource = new MapPropertySource("selfSource", SelfConfigContext.getInstance().getCache());
environment.getPropertySources().addFirst(propertySource);
}
}
接下来注册这个扩展点,直接选择在项目启动时,进行注册
@SpringBootApplication
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication springApplication = new SpringApplication(Application.class);
springApplication.addInitializers(new SelfConfigContextInitializer());
springApplication.run(args);
}
}
2. Environment配置刷新
envionment实时获取配置的方式,支持配置刷新应该相对简单,如直接吐出一个接口,支持更新我们自定义配置源的配置,不做任何变更,这个配置应该时同时更新的
首先提供一个Spring的工具类,用于更简单的获取Spring上下文
@Component
public class SpringUtil implements ApplicationContextAware, EnvironmentAware {
private static ApplicationContext applicationContext;
private static Environment environment;
private static Binder binder;
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
SpringUtil.applicationContext = applicationContext;
}
@Override
public void setEnvironment(Environment environment) {
SpringUtil.environment = environment;
binder = Binder.get(environment);
}
public static ApplicationContext getApplicationContext() {
return applicationContext;
}
public static Environment getEnvironment() {
return environment;
}
public static Binder getBinder() {
return binder;
}
}
配置更新的示例
@Slf4j
@RestController
public class IndexController {
@GetMapping(path = "update")
public String updateCache(String key, String val) {
SelfConfigContext.getInstance().updateConfig(key, val);
return "ok";
}
@GetMapping(path = "get")
public String getProperty(String key) {
return SpringUtil.getEnvironment().getProperty(key);
}
}
执行验证一下:
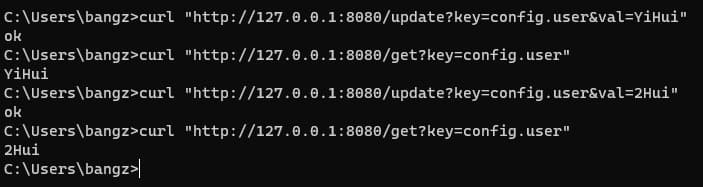
3. @ConfigurationProperties 配置刷新
之前在介绍自定义属性配置绑定时介绍过,通过Binder来实现绑定配置的Config对象动态刷新,我们这里同样可以实现配置变更时,主动刷新@ConfigurationProperties注解绑定的属性
具体实现如下,
@Slf4j
@Component
public class ConfigAutoRefresher implements ApplicationRunner {
private Binder binder;
/**
* 配置变更之后的刷新
*/
@EventListener()
public void refreshConfig(ConfigChangeListener.ConfigChangeEvent event) {
log.info("配置发生变更,开始动态刷新: {}", event);
SpringUtil.getApplicationContext().getBeansWithAnnotation(ConfigurationProperties.class).values().forEach(bean -> {
Bindable<?> target = Bindable.ofInstance(bean).withAnnotations(AnnotationUtils.findAnnotation(bean.getClass(), ConfigurationProperties.class));
bind(target);
});
}
/**
* 重新绑定bean对象对应的配置值
*
* @param bindable
* @param <T>
*/
public <T> void bind(Bindable<T> bindable) {
ConfigurationProperties propertiesAno = bindable.getAnnotation(ConfigurationProperties.class);
if (propertiesAno != null) {
BindHandler bindHandler = getBindHandler(propertiesAno);
this.binder.bind(propertiesAno.prefix(), bindable, bindHandler);
}
}
private BindHandler getBindHandler(ConfigurationProperties annotation) {
BindHandler handler = new IgnoreTopLevelConverterNotFoundBindHandler();
if (annotation.ignoreInvalidFields()) {
handler = new IgnoreErrorsBindHandler(handler);
}
if (!annotation.ignoreUnknownFields()) {
UnboundElementsSourceFilter filter = new UnboundElementsSourceFilter();
handler = new NoUnboundElementsBindHandler(handler, filter);
}
return handler;
}
@Override
public void run(ApplicationArguments args) throws Exception {
log.info("初始化!");
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = (ConfigurableEnvironment) SpringUtil.getEnvironment();
this.binder = new Binder(ConfigurationPropertySources.from(environment.getPropertySources()),
new PropertySourcesPlaceholdersResolver(environment),
new DefaultConversionService(),
((ConfigurableApplicationContext) SpringUtil.getApplicationContext())
.getBeanFactory()::copyRegisteredEditorsTo);
}
}
注意上面的实现,分三类:
public <T> void bind(Bindable<T> bindable): 具体实现绑定配置刷新的逻辑
核心思想就是将当前对象与environment配置进行重新绑定
public void run: binder初始化
在应用启动之后进行回调,确保是在environment准备完毕之后回调,获取用于属性配置绑定的binder,避免出现envionment还没有准备好
也可以借助实现EnvironmentPostProcessor来实现
public void refreshConfig(ConfigChangeListener.ConfigChangeEvent event): 配置刷新
通过@EventListener监听配置变更事件,找到所有的ConfigurationProperties修饰对象,执行重新绑定逻辑
接下来我们验证一下配置变更是否会生效
@Data
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "config")
public class UserConfig {
private String user;
private String pwd;
private Integer type;
private String wechat;
}
@Slf4j
@RestController
public class IndexController {
@Autowired
private UserConfig userConfig;
@GetMapping(path = "/user")
public UserConfig user() {
return userConfig;
}
@GetMapping(path = "update")
public String updateCache(String key, String val) {
selfConfigContainer.refreshConfig(key, val);
SelfConfigContext.getInstance().updateConfig(key, val);
return JSON.toJSONString(userConfig);
}
}
定义一个UserConfig来接收config前缀开始的配置,通过update接口来更新相关配置,更新完毕之后返回UserConfig的结果
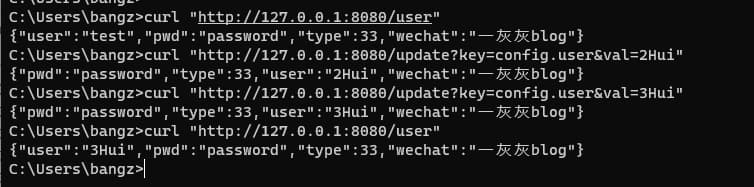
4. @Value 配置刷新
最后我们再来看一下@Value注解绑定的配置的刷新策略,很久很久之前我也介绍一篇博文,如何实现动态刷新,欢迎查看
其核心思想就是找出所有@Value绑定的成员变量,当监听到配置变更之后,通过反射的方式进行刷新
关键的实现如下
/**
* 配置变更注册, 找到 @Value 注解修饰的配置,注册到 SpringValueRegistry,实现统一的配置变更自动刷新管理
*
* @author YiHui
* @date 2023/6/26
*/
@Slf4j
@Component
public class SpringValueProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
private final PlaceholderHelper placeholderHelper;
public SpringValueProcessor() {
this.placeholderHelper = new PlaceholderHelper();
}
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
Class clazz = bean.getClass();
for (Field field : findAllField(clazz)) {
processField(bean, beanName, field);
}
for (Method method : findAllMethod(clazz)) {
processMethod(bean, beanName, method);
}
return bean;
}
private List<Field> findAllField(Class clazz) {
final List<Field> res = new LinkedList<>();
ReflectionUtils.doWithFields(clazz, res::add);
return res;
}
private List<Method> findAllMethod(Class clazz) {
final List<Method> res = new LinkedList<>();
ReflectionUtils.doWithMethods(clazz, res::add);
return res;
}
/**
* 成员变量上添加 @Value 方式绑定的配置
*
* @param bean
* @param beanName
* @param field
*/
protected void processField(Object bean, String beanName, Field field) {
// register @Value on field
Value value = field.getAnnotation(Value.class);
if (value == null) {
return;
}
Set<String> keys = placeholderHelper.extractPlaceholderKeys(value.value());
if (keys.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
for (String key : keys) {
SpringValueRegistry.SpringValue springValue = new SpringValueRegistry.SpringValue(key, value.value(), bean, beanName, field);
SpringValueRegistry.register(key, springValue);
log.debug("Monitoring {}", springValue);
}
}
/**
* 通过 @Value 修饰方法的方式,通过一个传参进行实现的配置绑定
*
* @param bean
* @param beanName
* @param method
*/
protected void processMethod(Object bean, String beanName, Method method) {
//register @Value on method
Value value = method.getAnnotation(Value.class);
if (value == null) {
return;
}
//skip Configuration bean methods
if (method.getAnnotation(Bean.class) != null) {
return;
}
if (method.getParameterTypes().length != 1) {
log.error("Ignore @Value setter {}.{}, expecting 1 parameter, actual {} parameters", bean.getClass().getName(), method.getName(), method.getParameterTypes().length);
return;
}
Set<String> keys = placeholderHelper.extractPlaceholderKeys(value.value());
if (keys.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
for (String key : keys) {
SpringValueRegistry.SpringValue springValue = new SpringValueRegistry.SpringValue(key, value.value(), bean, beanName, method);
SpringValueRegistry.register(key, springValue);
log.info("Monitoring {}", springValue);
}
}
}
上面的实现,主要利用到BeanPostProcessor,在bean初始化之后,扫描当前bean中是否有@Value绑定的属性,若有,则注册到自定义的SpringValueRegistry中
注意事项:
@Value有两种绑定姿势,直接放在成员变量上,以及通过方法进行注入
所以上面的实现策略中,有Field和Method两种不同的处理策略;
@Value支持SpEL表达式,我们需要对配置key进行解析
相关的源码,推荐直接在下面的项目中进行获取,demo中的实现也是来自apollo-client
接下来再看一下注册配置绑定的实现,核心方法比较简单,两个,一个注册,一个刷新
@Slf4j
public class SpringValueRegistry {
public static Map<String, Set<SpringValue>> registry = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
/**
* 像registry中注册配置key绑定的对象W
*
* @param key
* @param val
*/
public static void register(String key, SpringValue val) {
if (!registry.containsKey(key)) {
synchronized (SpringValueRegistry.class) {
if (!registry.containsKey(key)) {
registry.put(key, new HashSet<>());
}
}
}
Set<SpringValue> set = registry.getOrDefault(key, new HashSet<>());
set.add(val);
}
/**
* key对应的配置发生了变更,找到绑定这个配置的属性,进行反射刷新
*
* @param key
*/
public static void updateValue(String key) {
Set<SpringValue> set = registry.getOrDefault(key, new HashSet<>());
set.forEach(s -> {
try {
s.update((s1, aClass) -> SpringUtil.getBinder().bindOrCreate(s1, aClass));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
});
}
@Data
public static class SpringValue {
/**
* 适合用于:配置是通过set类方法实现注入绑定的方式,只有一个传参,为对应的配置key
*/
private MethodParameter methodParameter;
/**
* 成员变量
*/
private Field field;
/**
* bean示例的弱引用
*/
private WeakReference<Object> beanRef;
/**
* Spring Bean Name
*/
private String beanName;
/**
* 配置对应的key: 如 config.user
*/
private String key;
/**
* 配置引用,如 ${config.user}
*/
private String placeholder;
/**
* 配置绑定的目标类型
*/
private Class<?> targetType;
public SpringValue(String key, String placeholder, Object bean, String beanName, Field field) {
this.beanRef = new WeakReference<>(bean);
this.beanName = beanName;
this.field = field;
this.key = key;
this.placeholder = placeholder;
this.targetType = field.getType();
}
public SpringValue(String key, String placeholder, Object bean, String beanName, Method method) {
this.beanRef = new WeakReference<>(bean);
this.beanName = beanName;
this.methodParameter = new MethodParameter(method, 0);
this.key = key;
this.placeholder = placeholder;
Class<?>[] paramTps = method.getParameterTypes();
this.targetType = paramTps[0];
}
/**
* 配置基于反射的动态变更
*
* @param newVal String: 配置对应的key Class: 配置绑定的成员/方法参数类型, Object 新的配置值
* @throws Exception
*/
public void update(BiFunction<String, Class, Object> newVal) throws Exception {
if (isField()) {
injectField(newVal);
} else {
injectMethod(newVal);
}
}
private void injectField(BiFunction<String, Class, Object> newVal) throws Exception {
Object bean = beanRef.get();
if (bean == null) {
return;
}
boolean accessible = field.isAccessible();
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(bean, newVal.apply(key, field.getType()));
field.setAccessible(accessible);
log.info("更新value: {}#{} = {}", beanName, field.getName(), field.get(bean));
}
private void injectMethod(BiFunction<String, Class, Object> newVal)
throws Exception {
Object bean = beanRef.get();
if (bean == null) {
return;
}
Object va = newVal.apply(key, methodParameter.getParameterType());
methodParameter.getMethod().invoke(bean, va);
log.info("更新method: {}#{} = {}", beanName, methodParameter.getMethod().getName(), va);
}
public boolean isField() {
return this.field != null;
}
}
}
SpringValue的构建,主要就是基于反射需要使用到的一些关键信息的组成上;可以按需进行设计补充
到此,关于@Value注解的配置动态刷新就已经实现了,接下来写几个demo验证一下
@Slf4j
@RestController
public class IndexController {
@Value("${config.type:-1}")
private Integer type;
@Value("${config.wechat:默认}")
private String wechat;
private String email;
@Value("${config.email:default@email}")
public IndexController setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
return this;
}
@GetMapping(path = "update")
public String updateCache(String key, String val) {
SelfConfigContext.getInstance().updateConfig(key, val);
return wechat + "_" + type + "_" + email;
}
}
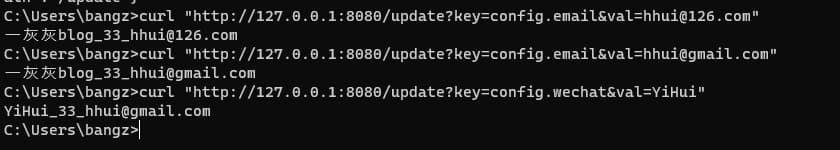
5. 小结
本文主要介绍了项目中配置的动态刷新的实现方案,也可以看作是apollo配置中心的简易实现原理,其中涉及到的知识点较多,下面做一个简单的小结
- 配置的三种使用姿势
@Value绑定@ConfigurationProperties绑定对象environment.getProperty()
- 自定义配置源加载
environment.getPropertySources().addFirst(MapPropertySource)
- 配置刷新
- Binder实现ConfigurationProperties刷新
- 反射实现@Value注解刷新